Artificial Intelligence
Maximizing the Lifespan of Your Idler Pulley
An idler pulley is a straightforward component found in many vehicles, primarily serving to maintain the proper tension on the accessory belt, also known as the "serpentine belt." Over time, this essential part experiences wear and tear, eventually leading to failure. Although replacement schedules for idler pulleys can vary depending on the vehicle, they typically need attention between 50,000 to 100,000 miles. Often, these replacements align with the recommended schedule for replacing the serpentine or accessory belt.
The Role of the Idler Pulley
While some vehicles do not incorporate an idler pulley, it is a fairly standard feature in modern cars. The accessory belt starts at the engine's crankshaft—usually positioned at the bottom—and powers various components like the air conditioning compressor and alternator. Positioned at the front of the engine, the belt rotates in sync with the engine's revolutions.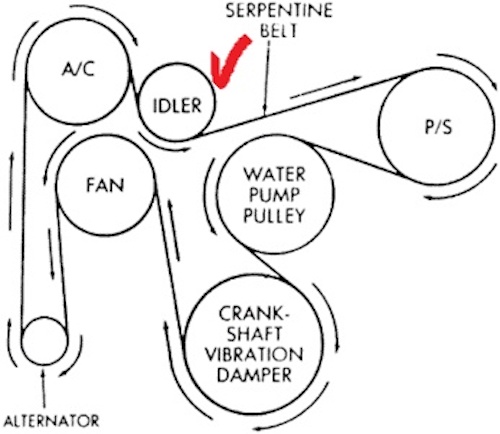
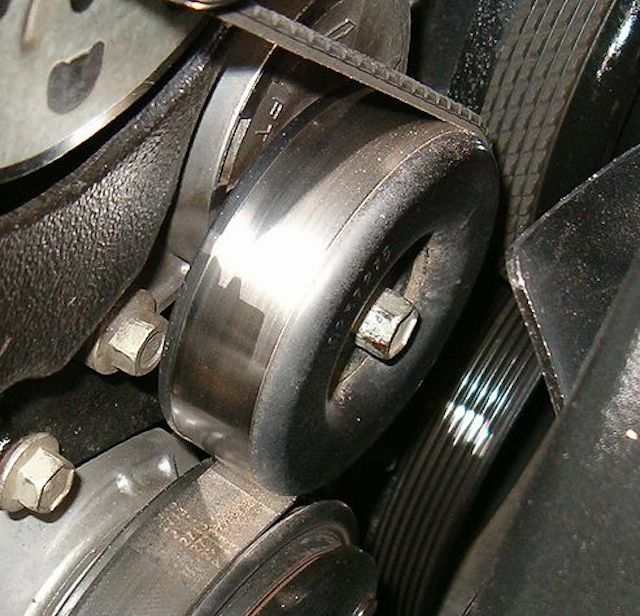

Image Copyright Una Smith
On most vehicles equipped with an idler pulley, the tension is adjusted by sliding the pulley along a rail-like mounting system and securing it in place. In other cases, a spring mechanism provides the needed tension, pressing the pulley firmly against the belt.Maintaining Proper Tension
The primary failure points for idler pulleys are usually the bearings that enable the pulley to rotate smoothly or the spring mechanism responsible for maintaining tension. To ensure the longest possible lifespan for your idler pulley, regular inspections are crucial. Any noticeable wobbling, squeaking, or excessive friction should prompt immediate replacement. The best approach to extending the idler pulley's life is to consistently monitor and adjust the tension on the serpentine belt. Additionally, always replace old belts with new ones when needed. This ensures the pulley operates optimally under its intended conditions while avoiding slippage or friction problems caused by a worn-out accessory belt.Replacing the Idler Pulley
The process of replacing an idler pulley varies depending on the specific vehicle model. The labor costs primarily involve removing and reinstalling the serpentine belt and the pulley itself. For experienced DIY enthusiasts, this task can be completed at home. Professional mechanics typically finish the job in under half an hour. In conclusion, while idler pulleys are relatively simple components, their role in maintaining optimal engine performance cannot be overstated. Regular maintenance and timely replacements are key to preventing unexpected breakdowns and ensuring smooth vehicle operation.Zhe Jiang RAF Electric Appliance Co.,ltd. , https://www.ackiliss.com